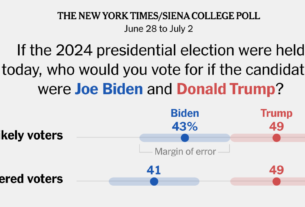
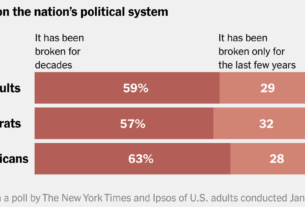
After President Trump left the White House in 2021, critics of his norm-breaking use of executive power implored Congress to tighten legal limits on when presidents can unilaterally reshape American government with the stroke of a pen. But lawmakers largely did not act.
On Monday, as Mr. Trump took the oath of office to begin his second term, he asserted a muscular vision of presidential power. He not only revived some of the same expansive understandings of executive authority that were left unaddressed, but went even further with new claims of sweeping and inherent constitutional clout.
Among a blizzard of executive orders, Mr. Trump instructed prosecutors not to enforce a law that bans the popular social media app TikTok until its Chinese owner sells it. President Joseph R. Biden Jr. had signed the measure into law after it passed with broad bipartisan support, and the Supreme Court unanimously upheld it.
Whatever the law’s merits, the Constitution says presidents “shall take care that the laws be faithfully executed.” Mr. Trump offered no clear explanation for how he has any legitimate power to instead suspend the law, making only a vague gesture toward his “constitutional responsibility” for national security, foreign policy “and other vital executive functions.”
Unilateral actions like emergency declarations and executive orders cannot create new legal powers for a president. Instead, they are a vehicle by which presidents exercise legal authority they already have, either because the Constitution has bestowed it upon their office or because Congress passed a law creating it.
That said, there are often disputes about the proper interpretation of the scope and limits of executive power. It is not uncommon for a president to use an executive order to take some action whose legal legitimacy is contested, leading to court fights that ultimately come before the Supreme Court.
It is not clear that anyone opposed to suspending the TikTok law would have standing to sue. But many of Mr. Trump’s moves concerned immigration law, making it very likely that legal challenges will follow and the legitimacy of his executive power claims will land before judges.
In several orders, Mr. Trump invoked his constitutional role as the military’s commander in chief, portraying migrants as invaders while blurring the line between immigration law enforcement and war powers.
“As commander in chief, I have no higher responsibility than to defend our country from threats and invasions, and that is exactly what I am going to do,” he said in his inaugural speech.
Among those orders, Mr. Trump declared that newly arriving migrants may not invoke a law allowing them to request asylum. As a basis, he said the Constitution gave him “inherent powers” to “prevent the physical entry of aliens involved in an invasion into the United States,” in addition to citing a few vague provisions of immigration laws.
Another such order directed the U.S. Northern Command, which oversees military operations in continental North America, to swiftly draw up a plan for a “campaign” to seal the border “by repelling forms of invasion including unlawful mass migration, narcotics trafficking, human smuggling and trafficking, and other criminal activities.”
Mr. Trump and his advisers have talked about invoking the Insurrection Act to use troops as additional immigration agents at the border. But the order referred only to his constitutional power as commander in chief, raising the possibility that he is envisioning using troops for a military operation rather than to act as law enforcement.
Some of the orders were a return to fights over executive power that surfaced during Mr. Trump’s first term.
On Monday, Mr. Trump reprised a move from 2019 by declaring a national emergency at the border. He also invoked a statute that allows presidents, during an emergency, to redirect military funds for construction projects related to the exigency. His purpose, in 2019 and again now, was to spend more taxpayer money on a border wall project than lawmakers authorized.
Is there really an emergency that an extended border wall would address, and that would justify circumventing Congress’s role in deciding where to direct taxpayer money?
A wall does not address the main border problem in recent years: the overwhelming number of migrants requesting asylum, flooding the system and leading to lengthy backlogs for hearings. And over the past seven months, illegal crossings have plunged to the lowest levels since the summer of 2020, during the early phase of the coronavirus pandemic.
But facts matter little to whether or when it is legal for presidents to invoke emergency power, declarations that are governed by the National Emergencies Act of 1976.
That law does not tightly define the circumstances under which presidents may determine that an emergency exists, leaving them with essentially unfettered discretion to unlock exigent powers for themselves. But previous presidents adhered to norms of self-restraint.
In his first term, critics challenged the legal legitimacy of Mr. Trump’s border wall spending, but the Supreme Court never resolved the dispute before Mr. Biden took office and canceled the projects. So any new legal challenge would have to start from scratch.
In the wake of Mr. Trump’s first term, House Democrats in 2021 passed a bill that would have tightened limits on presidential use of emergency powers, part of a package of reforms they called the “Protecting Our Democracy Act.” But Republicans opposed the measure as a partisan attack on a president who was no longer in office anyway, rendering it dead on arrival in the Senate.
Mr. Trump’s absence from the presidency, however, turned out to be temporary.
In the show of force upon his return to office, he also declared a national energy emergency so that, as he said in his inaugural speech, “we will drill, baby, drill.” No president has declared that type of emergency before, and it empowers him to suspend legal protections for the environment and to speed up permits for new oil and gas projects.
The nation’s energy situation hardly seems like an emergency: The United States is producing more oil than any country ever has, in no small part because of the fracking boom and because of thousands of new permits to drill on federal lands issued by the Biden administration — outpacing Mr. Trump’s first-term record. Prices for gasoline, natural gas and electricity are relatively low compared with their historical levels.
But the order said Mr. Trump had determined that Biden administration policies had “driven our nation into a national emergency, where a precariously inadequate and intermittent energy supply, and an increasingly unreliable grid, require swift and decisive action.” He also cited a growing need for electricity to run computer servers for artificial intelligence projects.
Elizabeth Goitein, a director of the Brennan Center for Justice’s Liberty and National Security Program who has written extensively on presidential emergency power, predicted that many of Mr. Trump’s planned actions would be challenged in court.
“Emergency powers should never be used to address longstanding problems like unlawful migration that can and should be addressed through legislation,” said Ms. Goitein, who was among those calling on Congress to curb presidential power. “The bad news is that Congress failed to enact reforms to the National Emergencies Act that would have helped prevent such abuses.”
There is no dispute that Mr. Trump had legitimate authority to take other unilateral actions. The Constitution clearly gives presidents unfettered authority to grant pardons to people for federal criminal offenses or to commute their sentences, for example, so there is little doubt Mr. Trump had the power to grant clemency to all of the nearly 1,600 people charged or convicted of crimes in connection with the Capitol riot.
But Mr. Trump appeared to put forward novel or expansive interpretations of legal authorities in other ways.
He ordered his administration to make recommendations about whether to designate certain transnational gangs and drug cartels as “foreign terrorist organizations,” stretching a law that is intended for groups that use violence for geopolitical and ideological purposes to criminal groups that, while also violent, are motivated by profit.
He also set in motion the possibility of invoking the Alien Enemies Act of 1798 to summarily expel immigrants suspected of being members of drug cartels and transnational criminal gangs without full due process hearings. That law’s text seems to require a link to the actions of a foreign government, so it is not clear whether the courts will allow Mr. Trump to invoke it to deny deportation hearings to people.
Mr. Trump is also seeking to change the basic understanding of a provision of the Constitution’s 14th Amendment that grants citizenship to most babies born on American soil and “subject to the jurisdiction” of the U.S. government. That provision has long been understood to include infants born to undocumented parents.
In an order, Mr. Trump invoked a theory developed by conservatives who want to curtail so-called birthright citizenship because they see it as a magnet for illegal immigration. By that rationale, the provision could be interpreted to not apply to babies whose parents are not American citizens or lawful permanent residents, even though visitors or undocumented people are subject to the jurisdiction of government prosecutors if they break the law.
Mr. Trump instructed agencies to refrain from issuing citizenship-affirming documents — like passports and Social Security cards — to infants born to undocumented immigrants or to parents lawfully but temporarily visiting the United States, starting with births 30 days from now.
Hours later, critics, including a coalition of Democratic-controlled states, brought multiple court challenges against it. Mr. Trump, the coalition asserted, sought to breach “this well-established and longstanding constitutional principle by executive fiat.”
It was yet another legal claim that seemed destined to come before the Supreme Court.